Buying items at wholesale prices and selling them on a retail model always brings up the most basic question: What should be the retail prices of those items and how much profit should you earn per product?
Retailers, especially the e-commerce sellers, always seem to be unsure about the sweet spot where they could earn a good profit margin per product and liquidate all the items they bought from wholesalers.
In this article, we will settle this long-standing debate of wholesale vs retail price, once and for all.
Let’s begin.
What Is Wholesale and Wholesale Price?
Wholesale is the business model in which a supplier sells the products in higher quantities at a lower price per product. A wholesale supplier may be a manufacturer, distributor, or stockist (middleman).
They have products in large quantities and are interested in selling them in batches or MOQs of relatively smaller quantities to multiple retailers.
Let’s understand this with an example that would present an overview of the wholesale business model and how the wholesale pricing is set.
Suppose you buy pet shoes at wholesale price from Alibaba. As Alibaba is one of the most prominent online wholesale selling platforms, most retailers, especially the e-tailers, buy products from this platform.
As per the below screenshot, the price of HC Pet Shoes is $11.40 per piece if you buy from 10 to 4,999 pieces. The price per pair drops to $9.20 if you buy 5,000 or more pieces.
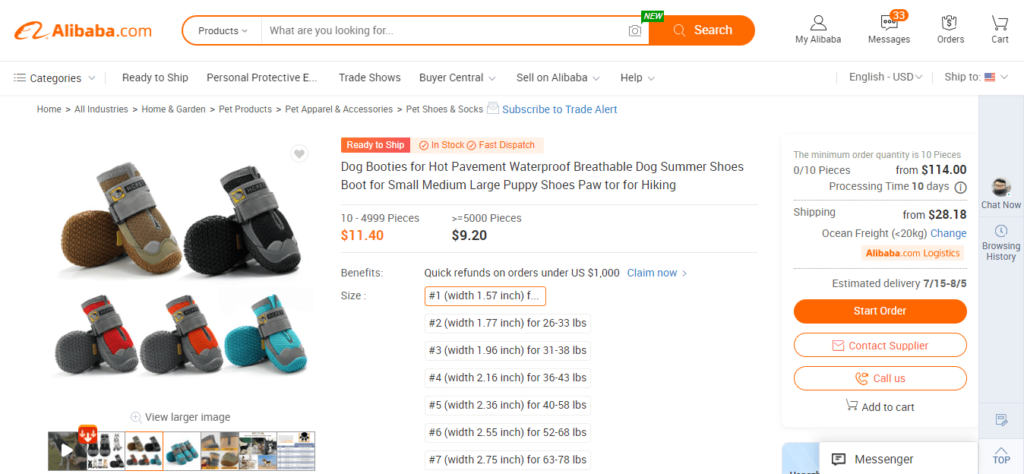
This difference of $2.2 per piece gives the retailer a chance to earn more profit margin per product if he buys in bulk quantity from this supplier.
As you can see, you cannot buy a single piece or pair.
Even if you don’t want to avail the discount of $2.2 per piece by buying more than 5,000 pieces, you would still have to adhere to the supplier’s minimum order quantity of 10 pieces.
A retailer can still sell these pet shoes at higher rates even if he buys 10 pieces from this wholesale supplier.
It is a win-win situation for both parties. The suppliers would be happy to sell more pieces to the retailer and the retailer would be happy to earn more profit margin per piece by selling these pet shoes to the consumers in lower quantities at higher prices.
Let’s discuss retail in detail.
What Is Retail and Retail Price?
Retail is a business model in which a retailer buys products from the wholesale supplier in higher quantities and sells them to the consumers or end-users in lower quantities as desired by the consumers (one by one).
A retailer is also called a reseller because he is reselling the products in lower quantities that he had bought in higher quantities.
A retailer sells products at a higher price per unit as compared to the price per unit he bought those products from the wholesale supplier.
That’s the cornerstone of the retail business model – to be profitable.
The retail price refers to the price of the product at which the consumer buys from a retailer or a reseller.
You will get more clarity about the retail business model and its pricing by reviewing the following example.
While Alibaba is one of the largest online wholesale selling platforms (B2B), Amazon is the largest online retail platform (B2C) in the world. Let’s learn about the retail pricing on Amazon.
Recall the example of HC Pet Shoes that we discussed above in the wholesale business. Following is the screenshot from the Amazon website for the same product.
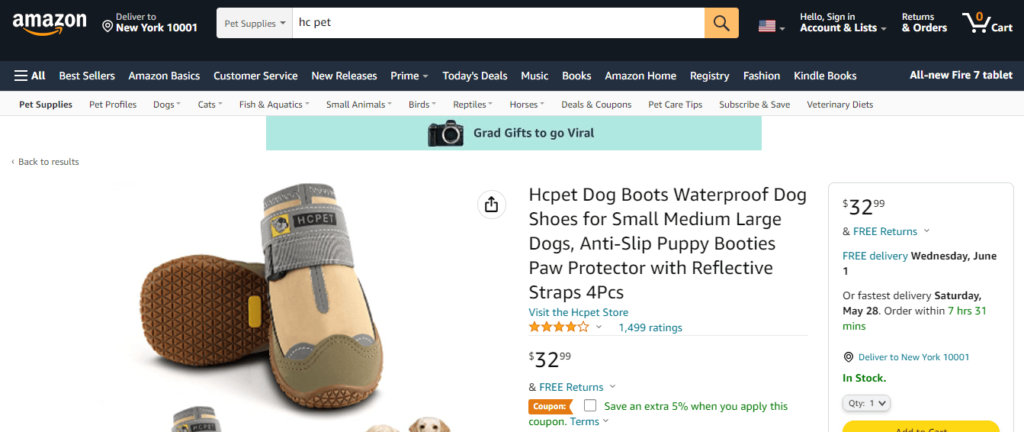
You can see that the same shoes are being sold on Amazon for $32.99 per 4 pcs. That means that the price of 2 pcs (1 pair) is around $16.5.
Considering that the retailer had bought this product for a maximum discounted price from the wholesaler ($9.20 for 5000+ pcs), he is having a gross profit of $7.3 per product.
Even if the retailer had bought the minimum order quantity of 10 pieces at $11.40, he is still saving around $5.1 per product.
Let’s check the same product on Alibaba’s own retail network, AliExpress.
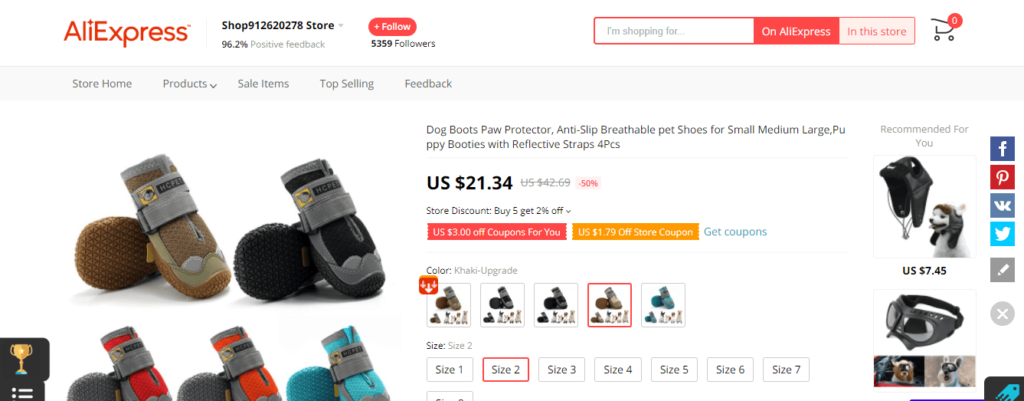
As you can see in the above screenshot, this retailer on AliExpress is selling the same shoes for $21.34 per 4 pcs. That makes the $10.67 retail price for 2 pcs (1 pair).
So, even if the same wholesale supplier from Alibaba has also listed himself here on AliExpress as a retailer for the same shoes, he is charging at least $1.47 more per pair at the retail (compared to $9.40 per pair).
Note: The above calculations of gross profits do not include business expenses.
Differences between Wholesale Price and Retail Price
Just to clarify the concepts of wholesale and retail prices, we have mentioned the following the differences between both.
- Wholesale prices are set for the retailers. Retail prices are set for the consumers or end-users.
- In most cases, the wholesale price per product is lower than the retail price per product.
- Wholesale prices come with minimum order quantities. Retail prices have no minimum order compulsions.
- Wholesale prices are generally backed by a bigger business (manufacturer or distribution network, etc.) while retail prices may be set by smaller businesses (grocery stores, online shops).
- Wholesale items are mostly niche-specific. One wholesaler may be dealing in one product only while the retailers tend to sell a mix of items together (a general store).
- Wholesale selling is simple. Retail selling is complex and requires a lot of selling techniques to attract customers.
- There are fewer customers to deal with in wholesale selling while retail selling requires dealing with a lot of customers.
Wholesale vs Retail: How to Calculate Prices and Profit Margins?
The calculation for wholesale and retail prices and profit margins is not that simple. Both businesses have different dynamics.

While you are at liberty to set the prices as per your sweet will to earn your dream profit margin, you may not want to do so. You have to do the competitor analysis and set the prices so that you remain competitive in the market.
At the same time, you cannot just subtract the selling price from the purchase price to calculate your profits. You have to include the expenses to calculate the true or net profit margins.
Let’s try to develop an understanding of the profit margins in both types of businesses.
How to Calculate the Wholesale Prices and Profit Margins?
In case the wholesale supplier is a manufacturer, he has to incur the costs of manufacturing those goods to set the wholesale price to be profitable.
The typical costs that a manufacturer has to include in setting the wholesale price are as follows.
- Cost of raw materials
- Cost of machinery
- Operational costs including electricity charges, etc.
- Labor costs
- Miscellaneous business expenses
In a simpler calculation, all of the above-mentioned costs are added and their sum is then divided by the number of pieces manufactured to calculate the cost per product.
For example, if the total cost of manufacturing 100,000 pairs of dog shoes is $500,000, then the cost to manufacture one pair of dog shoes would be $5.
It depends on the manufacturer which pricing strategy he wants to adopt. We will discuss the pricing strategies later in this article.
If he wants to earn a minimum of $4 per pair of dog shoes, he would sell one pair of dog shoes for $9 conditioning it with an MOQ.
How to Calculate the Retail Prices and Profit Margins?
Let’s take the example of the same dog shoes ahead for a clear understanding of wholesale and retail pricing.
One thing is clear by now. The retail price for the same dog shoes would be higher than its wholesale price of at least $9 per pair if a retailer wants to be profitable.
But at what price the retailer would sell a pair of those shoes?
It mainly depends on the market competition for that product. There would be many other retailers already selling that product.
In a special case, if there is no competition for that product, the retailer has the leverage to sell that item at higher retail prices.
But in normal circumstances, the retail price is in accordance with the market pricing for the product with the same or similar specifications.
We would discuss the pricing strategies in the coin section of this article.
In a typical case, a retailer would calculate the cost of goods including the price at which he had bought those items, and would add his desired profit margin to set the retail price of that product.
So, a simple retail price formula would be as follows.
Retail Price = Cost of Goods + Profit Margin
Fast Fact: If the retail price of a product becomes much higher than the prevalent market price, a retailer has to either cut down the cost of goods or the profit margin to be competitive in the market.
The costs of goods for a typical retailer would mean the total cost for the goods to reach the desired destination.
These costs can include the wholesale price of the product, shipping costs, customs duties, etc.
We can derive the simple formula for calculating the profit margin for the retailer from the retail price formula shared above.
Profit Margin (Retail) = Retail Price – Cost of Goods

If a retailer wants to calculate the real profit margin, he would have to include the operational costs required to sell the product.
In e-commerce, a retailer would have to include the costs of advertising and platform charges, etc to calculate the real profit margin.
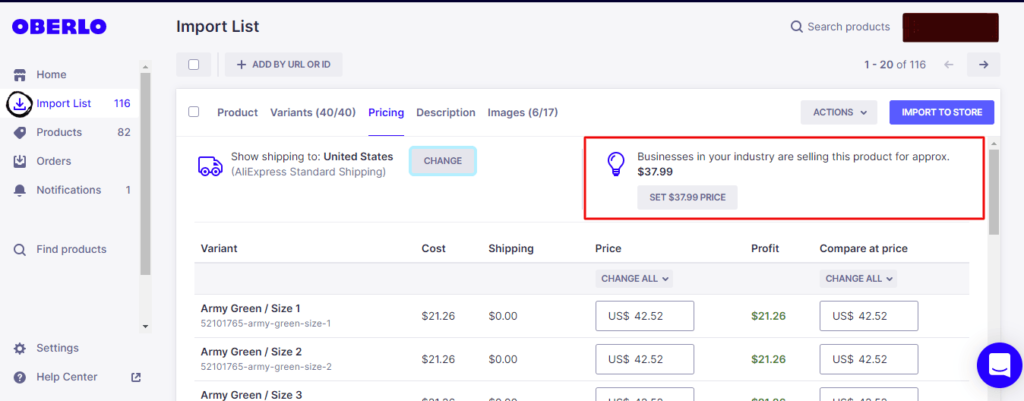
Fortunately, there are some apps like Oberlo that help you in suggesting the retail prices for your products.
Based on their intelligent algorithms and data collection, they check the retail prices of the same products from other retailers using their platform and suggest what price you should set for your products.
If you are not sure about what retail price you should set for a product, you can use these suggested retail prices.
Wholesale and Retail Pricing Strategies
Let’s go through the most common wholesale and retail pricing strategies that sellers use to set wholesale and retail prices.
Absorption Pricing Strategy
Absorption is one of the most common pricing strategies. In this strategy, the price includes all the costs of goods and the profit margin per product.
It is called absorption because all the pricing factors are absorbed into one final pricing.
Pros of Absorption Pricing Strategy
- Easy calculations
- Confirmed profits as per your wish
- Unaffected by external factors
Cons of Absorption Pricing Strategy
- The prices are not set against the competition.
- The prices can be unrealistic.
- Prices may be too high as per the buyer’s expectations.
Demand-based Pricing Strategy
The demand-based pricing strategy involves the pricing to be set as per the buyers’ demands.
If the demand for a particular product is high at a certain time, the price of that product will also be high and vice versa.
This strategy is also called time-based, differentiated, or seasonal pricing. That’s because the prices of the products may change as per the demand, season, or specific time of the year (Christmas, Halloween, etc.)
Fast Fact: This pricing strategy is not always upward. The wholesale prices may also go down in some cases. Factors like low demand, product saturation, and dead stock could force a wholesaler to lower the prices to get rid of stock.
Pros of Demand-based Pricing Strategy
- Demand-focused pricing can lead to earning high-profit margins.
- It can come with buyer acceptance to pay premium prices at the time of peak demands.
- Filling the demand gap at the right time can scale your wholesale business.
Cons of Demand-based Pricing Strategy
- Charging your customers with a premium can affect your repeat sales.
- Your brand reputation is at stake.
Competitive Pricing Strategy
As the name suggests, the competitive pricing strategy suggests setting the price of the products as per the prices set by your competitors in the market for the same or similar product.

The main idea behind this strategy is to remain competitive in the market so that you don’t lose costumers to your competitors being too high in prices as compared to them.
Pros of Competitive Pricing Strategy
- The sales are guaranteed as there is already competition.
- You have a clear idea of the price range. You don’t have to go through the price testing phase.
- You already have the leverage of buyers’ willingness to purchase those products at competitive prices.
Cons of Competitive Pricing Strategy
- You can be a loss leader if you set the prices lower than your costs just to be competitive. Your competitors may be earning profits in other products by lowering the prices of products that you are also selling while you may not have this option.
- You don’t have the opportunity to earn premium profits in this strategy.
FAQs about the Wholesale and Retail Price
Read the answers to the following frequently asked questions to have a clear understanding of wholesale and retail prices.
How Much Cheaper Is Wholesale than Retail?
There is no perfect rule as to how much cheaper should be the retail price from wholesale. But according to general practice, the wholesale price is at least 30-50% cheaper than retail because the products in wholesale are generally bought in bulk quantities.
This percentage of increase in the wholesale price is also known as wholesale markup.
Is Wholesale Price Usually Half of Retail?
Yes. But not always. If you compare most retail prices with their wholesale prices, you will notice that the wholesale price is almost 50% less than the retail.
That’s why the short-term e-commerce business owners who are just testing out the products, use this plain formula of setting the retail price as double the wholesale price.
Is Wholesale Price the Same as Cost Price for the Retailer?
Not exactly. The wholesale price of the products usually adds to the major portion of the product’s cost for the retailer.
But other cost factors like the shipping, customs, operational, and advertisement costs also translate into the total costs for the retailer.
Does the Wholesale Price Include Tax?
Yes. The wholesale prices charged by the suppliers usually include all forms of taxes to export the product from his country. But you have to pay the import duties or taxes set by your country at the time of product arrival at the port.
Summary
The wholesale vs retail prices are deeply related to each other. The wholesale price is the initial contributor to the retail price which is set after incorporating other costs and profit margin.
We have shared the most prevalent pricing strategies according to the business norms. You may still observe the dramatic fluctuations in the wholesale and retail prices for the same or related products in special cases.
If you want to source wholesale products at the most affordable prices, ask for a free quote and one of our experts will be there to come up with the best solutions for your business.

